Absorption Heat Pumps
HEAT PUMP
A heat pump is a device that draws heat from a lower-temperature heat source to a higher-temperature cooler. Like any other pump, an external source is needed for pumping; the energy source can be either steam, hot water, exhaust gas or fuel.
Heat pumps drive the heat from a lower temperature to a medium temperature using high-quality energy. Heat pumps use steam, hot water, exhaust gas, fuel, geothermal energy or any combination of these heat sources to pump heat. Heat pumps save approximately 35% of heat energy.
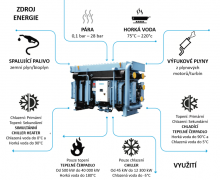
Absorption heat pumps - Following Absorption cooling for comfort cooling and chilled water production, absorption technology can also be applied to heat pumps to ensure hot water or steam production.
Operating range
- Output: 0.25–40 MW
- Hot water temperature: up to 90°C (194°F)
- High-quality heat source: Exhaust gases, steam, hot water and liquid/gaseous fuels (individually or in combination)
- COP: 1.65–1.75
- 4–10 bar.g Steam (pressure)
- Low-temperature heat sources (30°C – 60°C):
Low-temperature heat sources (30°C – 60°C):
•Water from a cooling tower
•Condensate from industrial process
High-temperature heat sources:
•Dry saturated steam (1-10 bar.g)
•Overheated water (130°C – 180°C)
•Flue gas (275°C – 600°C)
•Natural gas
Hot water production for users up to 90°C, COP 1.65–1.75